Latest News
Researches suggested that Vitamin D deficiency could lead to infertility!
LWH has fond out 35% of Taiwan women has Vitamin D deficiency, which could lead to infertility
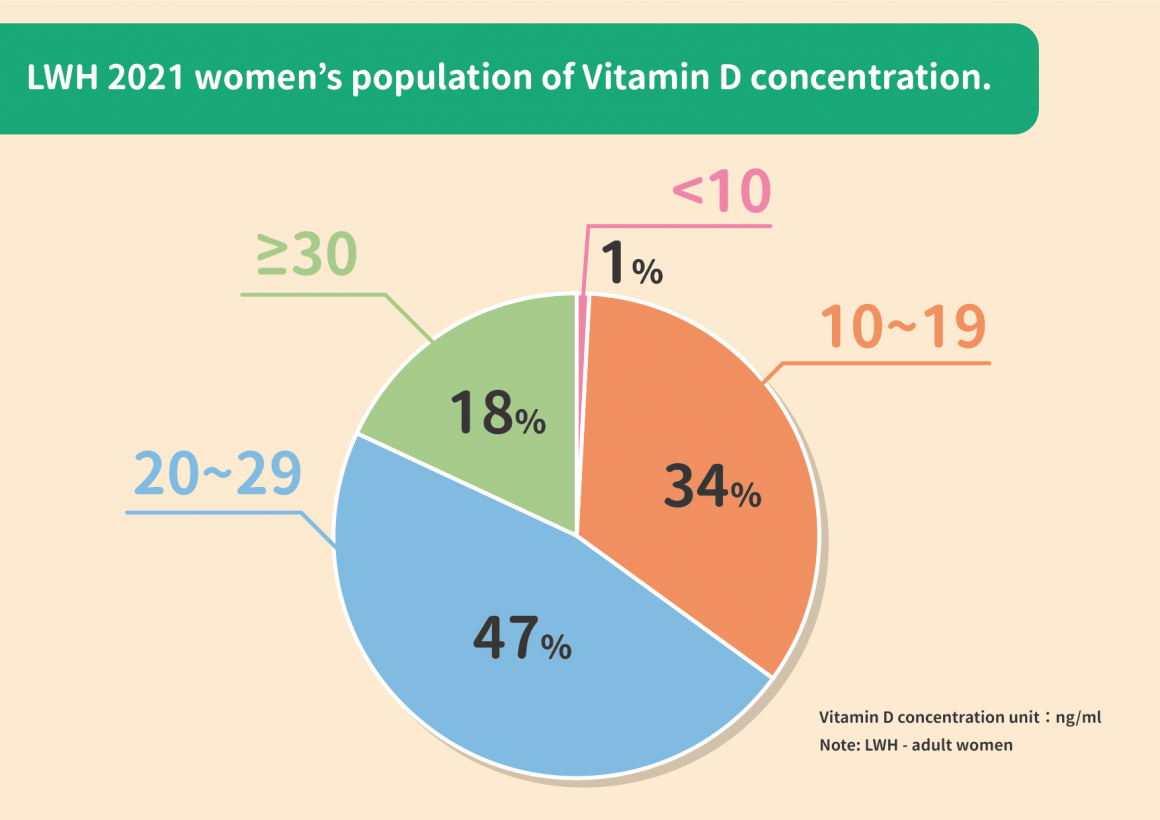
LWH has conducted a statistical analysis on 3802 adult women in 2021 and found out that the group with a extreme low Vitamin D concentration (<10ng/ml) is accounting for 1%; the low Vitamin D concentration of 10~19ng/ml which is a deficiency, was raised to 34% ; the proportion of those who were slightly low Vitamin D (20~29ng/ml) concentration was the highest, exceeding 47%; the proportion of women whose Vitamin D concentration reached the normal standard value was only 18%. Combining above data shows that the group with Vitamin D deficiency below 30ng/ml accounts for more than 82% of the total, that is, more than 8 out of 10 women have Vitamin D deficiency. This is a warning to the health of Taiwanese women.
The situation of Vitamin D deficiency on Taiwanese women is worse than the US, the UK and Canada
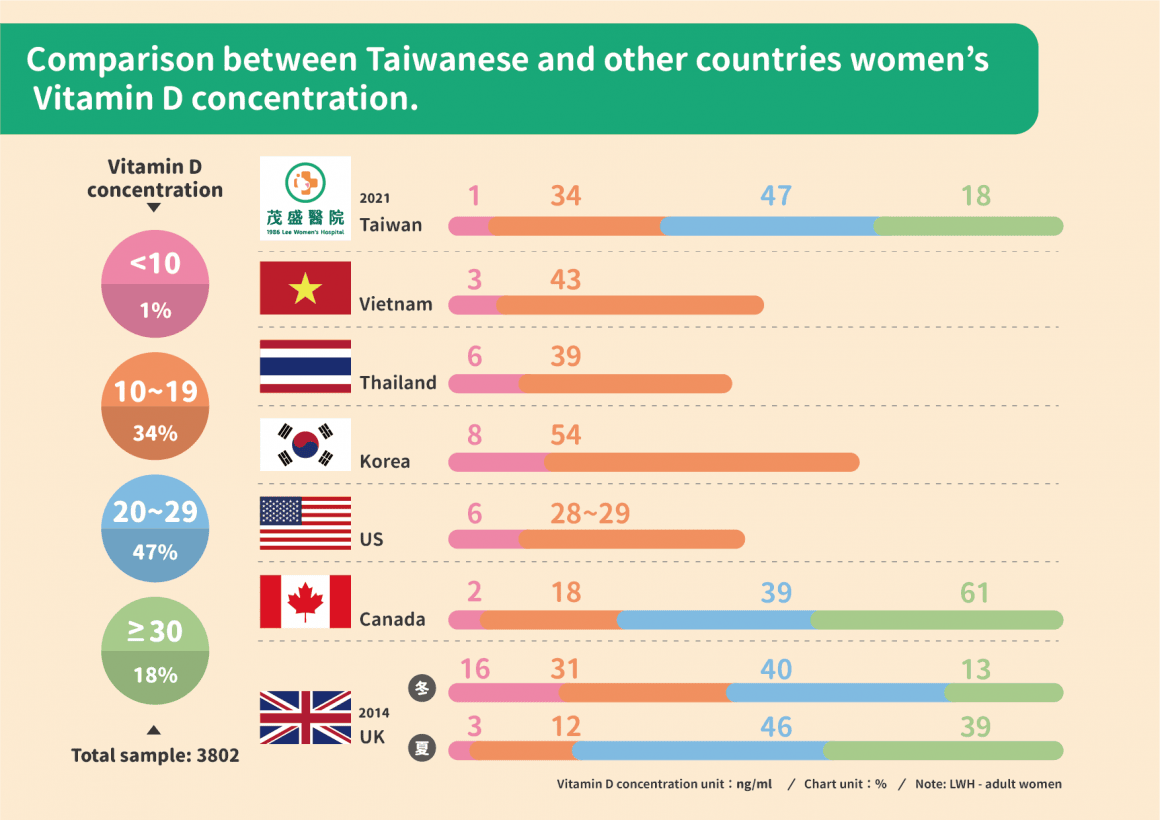
Dr. Lee explained from the 3802 cases, we have found that the proportion of women with Vitamin D concentration below 20ng/ml in the body is as high as 35%, which will affect the quality of eggs and the ability to conceive. According to the latest 2013-2016 survey reported by the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan, Dr. Lee pointed out that 39.7% of Taiwanese women of reproductive age (19 to 44 years old) have a Vitamin D concentration of <20ng/ml, which is similar to Vietnam, Thailand, etc. Compared with Southeast Asian countries, it is close; but compared with developed countries such as the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom, the Vitamin D concentration of women is much higher than that of Taiwan (Note 1). It is speculated that women in these areas with high latitudes and less sunshine have the habit of taking Vitamin D supplements. In view of the clinical research that a very high proportion of infertile women were found to be deficient in Vitamin D, Dr. Lee reminded them that it is necessary to supplement Vitamin D.
International paper points out that Vitamin D deficiency can affect the reproductive system and cause infertility
CEO of LWH Dr. Chun-I Lee cited in-hospital research and pointed out that the number of blastocysts, blastocyst rate and pregnancy rate of women with Vitamin D concentration ≥20ng/ml were about 50% higher than those of <20ng/ml (Note 2). International research papers have also demonstrated that women with Vitamin D deficiency may cause infertility, negative effects on ovaries, poor follicular development, poor egg quality, reduced fertility, etc. Men with low Vitamin D concentrations will also suffer from decreased sperm counts, low motility, reduced fertilization ability, etc. Other studies have also found that women undergoing IVF treatment with sufficient Vitamin D have significantly higher pregnancy rates. In addition, a serious lack of Vitamin D intake can lead to rickets in infants, and adults and the elderly are prone to Osteoporosis, Osteomalacia, Fractures, etc., so be careful!
Physician's recommendation: increase sun exposure, eat Vitamin D-containing foods or supplements to increase Vitamin D intake
It may be due to lack of sun exposure and insufficient intake of foods containing Vitamin D, which will cause more than 80% of Taiwanese women to have low Vitamin D concentrations. CEO Dr. Chun-I Lee, attending physician of department of reproductive and endocrinology, made a reasonable inference and put forward 3 suggestions to the public:
- Increase sun exposure: Noon is the time when the ultraviolet rays are the most abundant, you can wear T-shirt and shorts. Let the sun shine directly on the skin without applying sunscreen for 10 to 15 minutes, so that the body can synthesize Vitamin D by itself.
- Eat foods containing Vitamin D: salmon, sardines, tuna, mackerel, saury, tuna, oysters, shrimp, or mushrooms, black fungus, whole grains, milk, cheese, eggs (yolk), etc.
- Moderate intake of supplements: If you have difficulty in exposing under the sun and cannot get enough Vitamin D from your diet, you may consider taking supplements. According to the recommendation of the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Taiwan, adults should consume 800 to 2,000 IU (20-50µg) per day; if they want to help conceive, both men and women should supplement more than 2,000 IU of Vitamin D3 per day.
Dr. Lee advised that Vitamin D supplementation should be taken moderately. Excessive intake may lead to calcification of blood vessels and tissues, and also damaging the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, etc. It is recommended that people should discuss with their doctors before supplementing.
Note 1: Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?
Notes 2: Molecular actions of vitamin D in reproductive cell biology (Reproduction 2017/1;153:R29-R42)




