Knowledge Sharing
2024.04.11
Introduction to the Causes and Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts, Understanding the Chances of Pregnancy with Ovarian Cysts and Treatment Methods
What is an ovarian cyst? When there is an excessive amount of fluid within the ovaries.
The causes of ovarian cysts include hormonal imbalance, endometriosis, pelvic infection, etc. Symptoms vary depending on the location and type of the cyst. Rupture of the corpus luteum cyst is also something that must be paid attention to.
It can often be seen on Taiwan social platforms such as D-Card or PTT. Is surgery necessary if there is an ovarian cyst? How should they be treated? Can I get pregnant with ovarian cysts? Many people feel anxious when discussing the causes and symptoms of ovarian cysts. However, in fact, most ovarian cysts are benign and there are more than one classification.
This article will explain the symptoms, causes, and related knowledge of ovarian cyst surgery.
Ovarian cyst refers to the accumulation of fluid in the ovary. When the fluid is excessive or abnormal, it is called an "ovarian cyst" (commonly known as "hydroma"). Ovarian cysts can be formed into different types of cysts. The most susceptible group for ovarian cysts is women of childbearing age. The vast majority of ovarian cysts are benign and will disappear on their own within three months.
If it is a malignant ovarian cyst, it is called ovarian cancer. In the early stage of the disease, there are no special symptoms,making it difficult to be observed. If the malignant ovarian cyst has compressed the surrounding organs, you may experience abdominal tenderness, fullness, loss of appetite, and frequent urinary urgency. , menstrual disorders and pain during sexual intercourse.
Note: corpus luteum cysts more commonly rupture
At present, the more common case of ovarian cyst rupture is "corpus luteum cyst rupture". The corpus luteum cyst is especially prone to rupture during strenuous sexual intercourse because the corpus luteum cyst will be congested in the week before menstruation.
In addition, intense exercise and excessive blood accumulation in the cyst may also cause the cyst to rupture spontaneously (such as chocolate cyst rupture).
Pain or pressure: Accumulation of fluid within the cyst may cause pain by stretching the covering of the ovary, or the weight of the fluid may cause a sensation of pressure in the abdomen. Large ovarian cysts may lead to ovarian torsion, resulting in cell death, and require evaluation and treatment by a physician.
following symptoms:
The recurrence rate of endometriosis (chocolate cyst) after surgery is about 25% and will increase year by year. It may cause menstrual pain, pelvic pain, chronic inflammation, and cause adhesion in the pelvic cavity, making the surgery more difficult. Early treatment is required.

For overseas patients, please leave a message below or contact ivftaiwan@gmail.com
For patients in China, please add our official WeChat account of ivftaiwan01
For patients in Hong Kong and Macau, please contact ivftaiwan.hk@gmail.com
Any immediate or urgent inquiry, please dial +886-4-22347057 #1324
The causes of ovarian cysts include hormonal imbalance, endometriosis, pelvic infection, etc. Symptoms vary depending on the location and type of the cyst. Rupture of the corpus luteum cyst is also something that must be paid attention to.
It can often be seen on Taiwan social platforms such as D-Card or PTT. Is surgery necessary if there is an ovarian cyst? How should they be treated? Can I get pregnant with ovarian cysts? Many people feel anxious when discussing the causes and symptoms of ovarian cysts. However, in fact, most ovarian cysts are benign and there are more than one classification.
This article will explain the symptoms, causes, and related knowledge of ovarian cyst surgery.
What You May Want to Know About Ovarian Cyst Symptoms
- What is an ovarian cyst?
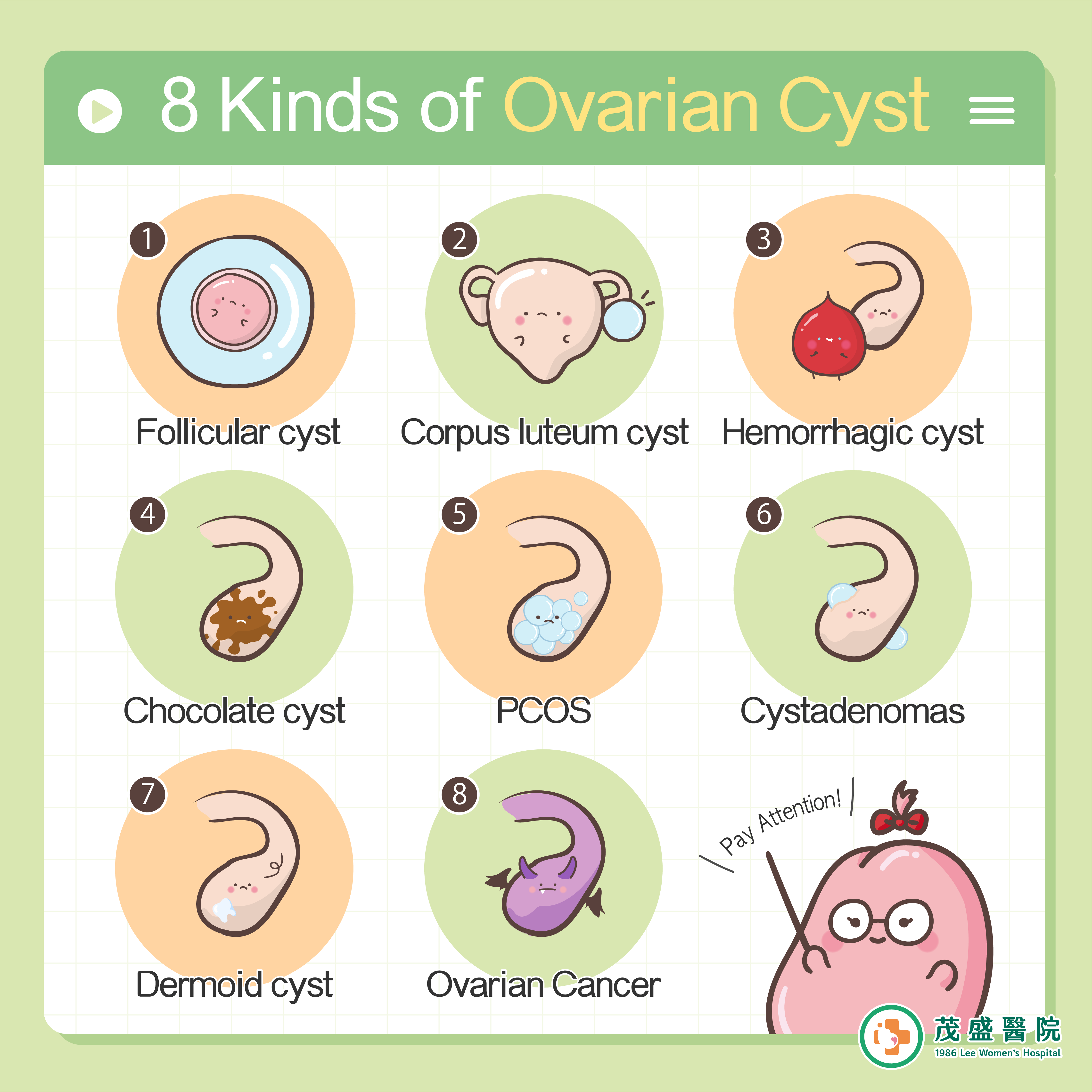
- Main categories of ovarian cysts
1. Functional cyst: follicular cyst, corpus luteum cyst
2. Hemorrhagic cyst
3. Chocolate cyst
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
5. Ovarian cystadenoma
6. Dermoid cysts
7. Ovarian cancer
Note: corpus luteum cysts more commonly rupture - What are the causes of ovarian cysts?
Who are the most prone groups to have ovarian cysts?
Is there a high chance of pregnancy with ovarian cysts? - What are the common symptoms of ovarian cysts?
How to deal with ruptured ovarian cyst? - Diagnosis and Treatment Methods for Ovarian Cysts:
How to diagnose ovarian cysts?
Should you see a doctor if you discover a 3-5 cm ovarian cyst?
Treatment options for ovarian cysts
How is ovarian cyst surgery performed? Are there any sequelae? - What can you eat if you have ovarian cysts?
If it is a malignant ovarian cyst, it is called ovarian cancer. In the early stage of the disease, there are no special symptoms,making it difficult to be observed. If the malignant ovarian cyst has compressed the surrounding organs, you may experience abdominal tenderness, fullness, loss of appetite, and frequent urinary urgency. , menstrual disorders and pain during sexual intercourse.

1. Functional cyst:
The most common cyst occurs in women of childbearing age during the ovulation cycle. It is formed by an abnormal amount of fluid and can be classified as follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst. It usually disappears on its own within three months.Follicular cyst:
Every month, the ovary produces a fluid sac that surrounds the egg, and when ovulation occurs, it ruptures and releases the egg into the fallopian tube. If the fluid sac does not rupture, it may continue to grow and become a follicular cyst. Most follicular cysts disappear within 8 weeks, and do not cause pain unless they are larger cysts.Corpus luteum cyst:
Due to hormonal effects, corpus luteum cysts usually form after ovulation and disappear within a few weeks. If the cyst is large, it may cause pain due to bleeding.Note: corpus luteum cysts more commonly rupture
At present, the more common case of ovarian cyst rupture is "corpus luteum cyst rupture". The corpus luteum cyst is especially prone to rupture during strenuous sexual intercourse because the corpus luteum cyst will be congested in the week before menstruation.
In addition, intense exercise and excessive blood accumulation in the cyst may also cause the cyst to rupture spontaneously (such as chocolate cyst rupture).
2.hemorrhagic cyst:
When a follicular cyst or corpus luteum cyst grows too fast, it will pull on the ovarian tissue and cause tearing and bleeding; the blood will accumulate in the ovary and is called a hemorrhagic cyst. Hemorrhagic cysts take a long time to disappear on their own, and only in rare cases require surgical removal.3. Chocolate cyst:
Also known as Endometriomas, endometrial tissue grows ectopically in the ovaries, forming a large amount of viscous brown liquid that looks like chocolate. Therefore, such ovarian cysts will increase in size over time and erode normal tissue, causing irreversible damage. They may affect ovarian function and make it difficult for patients to conceive. Surgery may be required after a doctor's evaluation.4. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS):
PCOS is a condition in which there are multiple cysts in the ovary at the same time. It usually does not cause harm or pain to the body, but it may affect pregnancy and must be evaluated and treated by a doctor.5. Ovarian cystadenomas (Cystadenomas):
Cysts that form from the ovarian epidermal tissue and are filled with fluid or mucus. Most patients will notice abdominal swelling and will not discover it until they go to the hospital for a medical examination.6. Dermoid cysts:
It is a congenital disease, originating from germ cells. It will not disappear on its own and may continue to grow. It is best to remove it as soon as possible.7. Ovarian cancer:
The chance of suffering from ovarian cancer is very low, but because it is located in the pelvic cavity, it is not easy to detect early.What are the causes of ovarian cysts?
There are four main causes of ovarian cysts:- Hormonal imbalance: Follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts may develop from hormonal abnormalities or the use of ovulation medications.
- Endometriosis: ectopic growth of endometrial tissue into the ovaries.
- Pregnancy: Usually it will disappear naturally in the second trimester of pregnancy. If it still exists in the later stages of pregnancy, it may need to be removed.
- Severe pelvic infection.
Who are the most prone groups to have ovarian cysts?
Ovarian cysts tend to occur in women aged 20 to 50, especially those with a family history of ovarian cysts.Is there a high chance of pregnancy with ovarian cysts?
In most cases, ovarian cysts do not affect pregnancy. If you have endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome, it will be difficult to conceive. It is recommended to go to the hospital to receive infertility treatment to increase the chance of pregnancy.Symptoms of ovarian cysts
It is possible to have no symptoms at all: It is recommended that women should have regular physical examinations and ultrasound examinations, which can help doctors determine the size and type of ovarian tumors.Pain or pressure: Accumulation of fluid within the cyst may cause pain by stretching the covering of the ovary, or the weight of the fluid may cause a sensation of pressure in the abdomen. Large ovarian cysts may lead to ovarian torsion, resulting in cell death, and require evaluation and treatment by a physician.
- Infertility: Ovarian cysts that can cause infertility are mainly polycystic cysts and endometriosis (chocolate cysts). You need to find an infertility specialist for further treatment.
- Menstrual disorders: Because cysts interfere with the normal secretion of ovarian hormones, ovarian cysts can lead to menstrual irregularities.
- Waist circumference becomes thicker or there is a foreign body in the abdomen: Patients often feel that they have become fatter and cannot fit into their clothes, or they feel a foreign body in the abdomen and seek medical advice.
- Frequent urination and constipation: Because the tumor squeezes the ureter, abdomen, intestines, kidneys, etc., it may cause frequent urination and constipation in patients.
following symptoms:
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Abdominal pressure and swelling
How to deal with ruptured ovarian cyst?
If an ovarian cyst ruptures, it can cause bleeding and severe pain. In severe cases, it can even lead to infection. If it causes acute abdominal pain, emergency surgery is required. If you find that you have persistent severe pain in your lower abdomen, it is recommended to go to the emergency room for examination and treatment immediately.Ovarian cyst diagnosis and treatment methods
How to diagnose ovarian cysts?
- Pelvic examination (Gynecological Examination)
- Ultrasound examination: Ultrasound examination of ovarian cysts can help doctors determine the size and type of ovarian tumors.
- Tumor Index: This examination may be arranged if malignancy is suspected.
Do I need to see a doctor if my ovarian cyst is found to be 3 cm or 5 cm in size?
- Ovarian cysts less than 5 cm (e.g. ovarian cysts 3 cm): Usually they will disappear on their own within three months, but it is still recommended to follow up regularly every two months for confirmation.
- If the cyst persists and is within 6 cm to 10 cm in size: if there are no uncomfortable symptoms, it is still recommended to go to the hospital for follow-up observation and examination.
- If the ovarian cyst continues to grow to more than 10cm or serious complications occur (ovarian torsion or ovarian cyst rupture): you should immediately follow the doctor's instructions and consider surgical treatment.
Ovarian cyst treatment methods
- Regular tracking: Most patients do not require treatment and only need regular ultrasound examinations to track changes in the cyst. The cyst usually disappears within three months.
- Surgical treatment: When ovarian cysts continue to grow to more than 8 cm or serious complications occur (ovarian torsion or ovarian cyst rupture), doctors will consider surgical treatment.
How is ovarian cyst surgery performed? Are there any sequelae?
Generally, laparoscopic surgery, traditional laparotomy or Da Vinci robotic arm surgery are used for ovarian cyst surgery. The surgical method will depend on the size, shape and stability of the patient's tumor, as well as the patient's need for future pregnancy.The recurrence rate of endometriosis (chocolate cyst) after surgery is about 25% and will increase year by year. It may cause menstrual pain, pelvic pain, chronic inflammation, and cause adhesion in the pelvic cavity, making the surgery more difficult. Early treatment is required.
How much does ovarian cyst surgery cost?
Both traditional laparotomy and laparoscopic surgeries for ovarian cysts can apply for health insurance in Taiwan. Only some medical materials need to be paid for at your own expense. The actual cost of ovarian cyst surgery can be evaluated and selected based on personal needs and physician recommendations.What can you eat if you have ovarian cysts?
Generally speaking, if you follow a regular diet and work schedule and maintain good living habits, there won't be any big problems. Try to pay more attention to the following two kinds of diet:1. Watch out for Sweets
If sweets are ingested for a long time, the insulin concentration will be too high, resulting in insulin resistance, which will lead to an increase in androgens in the blood, ovulation disorders, and polycystic ovary syndrome.2. Watch out for Fried food
Fried foods contain saturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and cholesterol, which can lead to hormonal disorders or disorders, leading to polycystic ovary syndrome, uterine fibroids, and endometriosis (chocolate cysts).
For overseas patients, please leave a message below or contact ivftaiwan@gmail.com
For patients in China, please add our official WeChat account of ivftaiwan01
For patients in Hong Kong and Macau, please contact ivftaiwan.hk@gmail.com
Any immediate or urgent inquiry, please dial +886-4-22347057 #1324




