Knowledge Sharing
2024.11.04
What Causes Uterine Fibroids and What Are the Warning Signs? A Doctor’s Guide to Surgery and Dietary Precautions
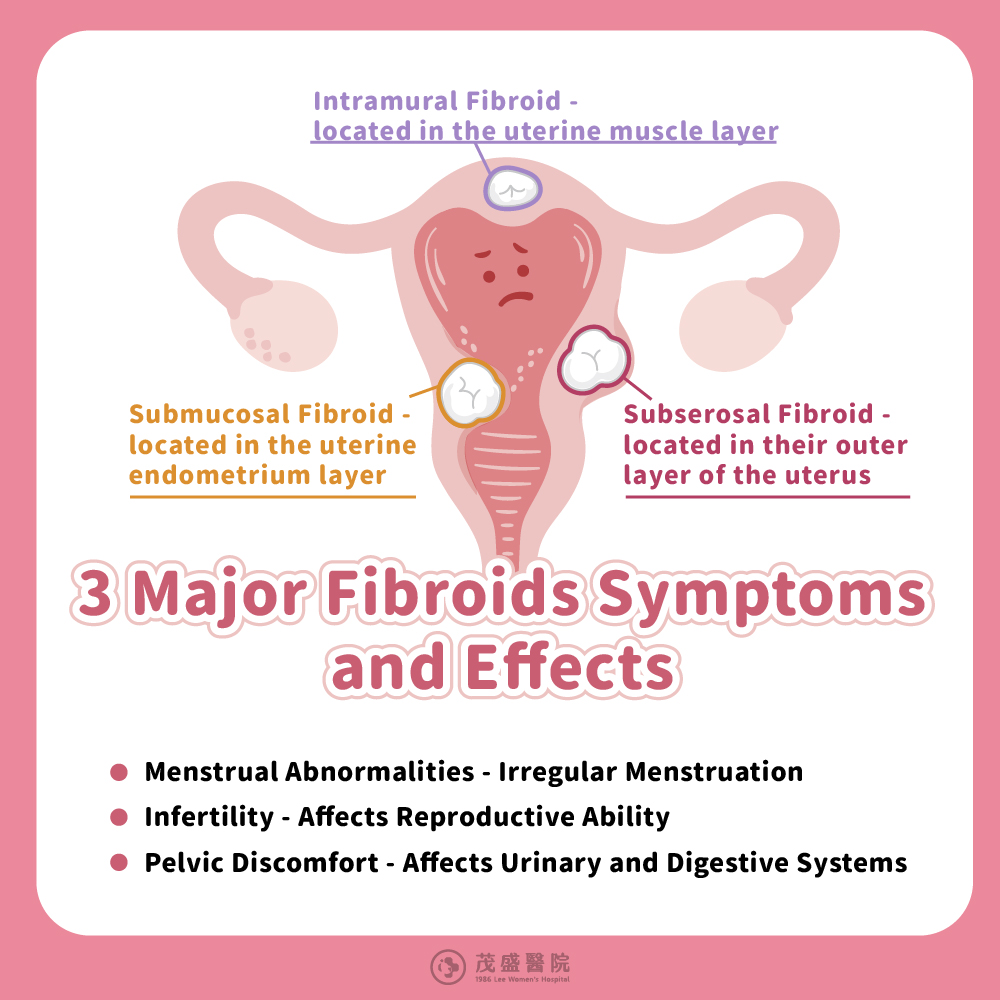
Uterine fibroids are categorized into different types based on their location within the uterus. Over 50% are intramural fibroids, found in the uterine muscle layer; 30-40% are subserosal fibroids, located on the outer layer of the uterus; and 10-20% are submucosal fibroids, situated beneath the uterine lining.
Fibroids Symptoms vary depending on the fibroid’s location. Intramural and submucosal fibroids, in particular, may affect fertility. This article will help you understand more about the causes, fibroids symptoms, and fibroids treatment options for uterine fibroids.
They typically occur between the ages of 35 and 45 and are classified as benign tumors. Uterine fibroids are named based on their location: subserosal fibroids, intramural fibroids, and submucosal fibroids, each with its own set of symptoms.
Additionally, research from the UK, USA, and Germany shows Black women to have a rate 3 to 4 times higher than other ethnic groups. A diet high in sugar and preserved foods is also associated with 3 times higher odds that women will develop fibroids.
Difficulty conceiving or infertility: Challenges with conception, miscarriage, preterm birth, etc., affecting fertility.
Pelvic discomfort: Pelvic pain, frequent urination, abdominal bloating, constipation, etc., impacting urinary and digestive functions.
Uterine fibroids are named based on their location, and we’ll explain these from the outermost layer to the innermost layer.
If a fibroid’s location compresses the fallopian tubes or blocks the uterine cavity, it can hinder sperm movement or embryo implantation. Fibroids may also cause abnormal uterine contractions and reduce endometrial receptivity. Additionally, fibroids reduce the elasticity of the uterine wall and divert blood flow, which can decrease blood supply to the uterus.
After fibroids are removed, the uterine environment often improves, increasing pregnancy rates. Whether fibroids require surgery depends on their size, location, and number. Regular Pap smears and ultrasound exams at the hospital are recommended.
2. Fibroids causing menstrual pain or excessive bleeding leading to anemia.
3. Fibroids causing pressure symptoms on the bladder or colon.
4. Rapidly growing fibroids (e.g., increasing from 2 cm to 4 cm within a few months).
5. Pedunculated or subserosal fibroids that may be at risk of torsion.
6. Intramural or submucosal fibroids compressing the fallopian tubes, leading to obstruction and infertility.
2. Women who are pregnant.
3. Women in menopause can be monitored regularly.
4. Women who have already reached menopause.
Avoid Environmental Hormone Pollution: Stay away from artificial chemicals in the environment that mimic human hormones, as they can interact with sex hormone receptors in the body. In daily life, try to avoid using plastic bags for food storage, using paper containers for hot food, and prolonged contact with printing inks.
High-Calcium Foods: These are good for uterine development and ovarian health.
Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Phytochemicals in plants can help reduce inflammation and inhibit tumor growth.
Consume Healthy Protein: This can regulate metabolic functions and promote normal hormone secretion, helping to prevent obesity.
2. Rapidly growing fibroids with suspicion of potential malignancy.
3. Fibroids that reach 7-8 cm in size, particularly in patients under 45 years of age who are not expected to undergo menopause within the next five years.
Begin pregnancy planning 3-6 months after undergoing hysteroscopic surgery.
Read more about the Great News (In Manderine):Woman conceived twins naturally after fibroid removal surgery.
Fibroids Symptoms vary depending on the fibroid’s location. Intramural and submucosal fibroids, in particular, may affect fertility. This article will help you understand more about the causes, fibroids symptoms, and fibroids treatment options for uterine fibroids.
Uterine Fibroids Overview
- What Are Uterine Fibroids?
- What Causes Fibroids and Early Signs
- Uterine fibroids Symptoms and Indicators
- Characteristics of Fibroids Based on Location
- Are Uterine Fibroids Related to Infertility?
- Diagnosis and Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids
- Uterine Fibroids Treatment
- When Is Surgery Necessary for Uterine Fibroids?
- How Is Surgery Performed for Uterine Fibroids?
- Dietary Precautions and Daily Care for Uterine Fibroids
- Precautions and Frequently Asked Questions About Uterine Fibroids
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are smooth muscle tumors that grow within the uterus and are the most common type of gynecological tumor, affecting over 30% of women.They typically occur between the ages of 35 and 45 and are classified as benign tumors. Uterine fibroids are named based on their location: subserosal fibroids, intramural fibroids, and submucosal fibroids, each with its own set of symptoms.
What Causes Fibroids and Early Signs
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is still unknown. Possible causes may include abnormal female hormones, excessive absorption of estrogen by uterine muscle tissue, genetics, or environmental factors.Additionally, research from the UK, USA, and Germany shows Black women to have a rate 3 to 4 times higher than other ethnic groups. A diet high in sugar and preserved foods is also associated with 3 times higher odds that women will develop fibroids.
Uterine fibroids Symptoms and Indicators
Possible symptoms of uterine fibroids include:- Menstrual cramps
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Anemia
- Prolonged menstrual periods
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent dizziness or fatigue
Signs and Effects of Uterine Fibroids
Menstrual abnormalities: Excessive menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, severe menstrual cramps, pain during intercourse, etc., leading to menstrual irregularities.Difficulty conceiving or infertility: Challenges with conception, miscarriage, preterm birth, etc., affecting fertility.
Pelvic discomfort: Pelvic pain, frequent urination, abdominal bloating, constipation, etc., impacting urinary and digestive functions.
Do Uterine Fibroids Cause Abdominal Pain?
If a fibroid larger than 5 cm is present during pregnancy, it may cause abdominal pain for the expectant mother. Hence, we recommend rest, bed rest, and adequate hydration to relieve fibroid-related abdominal pain. Along with that, if pain medication is needed, please consult your ob/gyn for evaluation first.Can Uterine Fibroids Disappear?
Fibroids may shrink when a woman approaches menopause and the oestrogen levels will decrease. Nonetheless, uterine fibroids cannot fully vanish.Characteristics of Fibroids Based on Location
Imagine the uterus as a room for a fetus. The muscle layer is comparable with the wall, the mucous membrane is like the interior decor or paint on the walls, while the serous layer represents the tiles on the outer wall, providing a slight separation from the outside.Uterine fibroids are named based on their location, and we’ll explain these from the outermost layer to the innermost layer.
1. Subserosal Fibroids
Located on the outer layer of the uterus, like tiles on the outer wall. These fibroids grow on the outside of the uterus and they do not cause uterine bleeding, but may press into the urinary and digestive tracts, affecting urination and bowel movements.2. Intramural Fibroids
Grows in the muscle layer, between the mucosa and serosa. This fibroid often leads to symptoms like heavy menstrual bleeding and prolonged periods.3. Submucosal Fibroids
Located on the inner side of the uterine wall, where the mucous membrane is shed with a period. Fibroids in this area often cause abnormal menstrual bleeding.
Are Uterine Fibroids Related to Infertility?
Uterine fibroids can affect pregnancy and may lead to infertility.If a fibroid’s location compresses the fallopian tubes or blocks the uterine cavity, it can hinder sperm movement or embryo implantation. Fibroids may also cause abnormal uterine contractions and reduce endometrial receptivity. Additionally, fibroids reduce the elasticity of the uterine wall and divert blood flow, which can decrease blood supply to the uterus.
After fibroids are removed, the uterine environment often improves, increasing pregnancy rates. Whether fibroids require surgery depends on their size, location, and number. Regular Pap smears and ultrasound exams at the hospital are recommended.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids
- Regular gynecological Examination: If a suspicious mass is detected on routine check-up, the doctor will arrange for further tests.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound is used to observe the size and location of the fibroids.
- Hysteroscopy: To allow for direct observation of the cervical canal and uterine cavity environment.
Uterine Fibroids Treatment
Uterine fibroids treatment is tailored according to the patient's symptoms and future fertility plans, mainly can be treated in 3 ways: regular monitoring, medication, and surgical treatment.- No Significant Symptoms with Future Fertility Plans: Regular Monitoring
If the patient has no significant symptoms and the fibroids are small, regular follow-up will be sufficient, as fibroids may shrink with menopause. - Symptoms Present with Future Fertility Plans: Medication
Medication for uterine fibroids is typically aimed at menstrual pain and excessive bleeding. Common medications include pain relievers, hemostatic agents, or oral contraceptives. - Severe Symptoms with Future Fertility Plans: Surgical Treatment
If symptoms cannot be relieved by medication or are severe, and the fibroids are larger than 5 cm, then a myomectomy may be considered to remove the fibroids. Patients can be evaluated at a fertility clinic to discuss further treatment options with a doctor. - Severe Symptoms without Future Fertility Plans: Surgical Treatment
If the patient does not plan to have children, a hysterectomy may be considered to prevent the recurrence of fibroids.
Medication Treatments for Uterine Fibroids
For asymptomatic uterine fibroids, observation is generally sufficient. Most medications aim to relieve symptoms and cannot eliminate fibroids, making surgery the primary treatment option. The types of medication for uterine fibroids include:
- Oral Contraceptives: Help alleviate excessive menstrual bleeding.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Relieve menstrual pain and improve excessive bleeding.
- Androgens: Help alleviate anemia caused by excessive bleeding.
- GnRH Agonists: Reduce the size of fibroids and decrease blood loss during surgery.
- Progesterone Receptor Antagonists: Improve abnormal bleeding and shrink fibroids.
When Is Surgery Necessary for Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids typically grow at an average rate of 0.5 to 1 cm per year. However, if a patient experiences fibroids growing 3 to 5 cm within a year, or if they increase from 2 cm to 4 cm within a few months and continue to grow, a physician should evaluate whether further examination is needed and if surgery is necessary.Indications for Surgery on Uterine Fibroids
1. Fibroids larger than 6 cm.2. Fibroids causing menstrual pain or excessive bleeding leading to anemia.
3. Fibroids causing pressure symptoms on the bladder or colon.
4. Rapidly growing fibroids (e.g., increasing from 2 cm to 4 cm within a few months).
5. Pedunculated or subserosal fibroids that may be at risk of torsion.
6. Intramural or submucosal fibroids compressing the fallopian tubes, leading to obstruction and infertility.
When Is Surgery Not Recommended for Uterine Fibroids?
1. Fibroids are small and symptoms are not severe.2. Women who are pregnant.
3. Women in menopause can be monitored regularly.
4. Women who have already reached menopause.
How Is Surgery Performed for Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroid surgery is mainly divided into 2 categories:1. Myomectomy:
This procedure involves the endoscopic removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus's ability to conceive. It is recommended that patients wait 6 months after the surgery before trying to get pregnant, and a cesarean section is advised during delivery to avoid the risk of uterine rupture. Statistics show that the recurrence rate of fibroids after myomectomy is approximately 15%, and there is a risk of scar tissue formation and adhesions in the endometrium.2. Hysterectomy:
This involves laparoscopic surgery to remove the entire uterus. The bleeding during this procedure is typically less than that of a myomectomy, and it effectively prevents the recurrence of fibroids while also reducing the risk of endometrial and cervical cancer.Dietary Precautions and Daily Care for Uterine Fibroids
Currently, there is no demonstrate method to prevent uterine fibroids, but avoiding long-term exposure to environmental hormone pollutants and being mindful of dietary habits can help reduce the likelihood of fibroids continuing to grow.Avoid Environmental Hormone Pollution: Stay away from artificial chemicals in the environment that mimic human hormones, as they can interact with sex hormone receptors in the body. In daily life, try to avoid using plastic bags for food storage, using paper containers for hot food, and prolonged contact with printing inks.
- Avoid Sitting Too Much: Engage in regular exercise 3 times a week for at least 20 minutes each session, maintaining a heart rate of over 60% of your maximum heart rate.
- Be Cautious with Nutritional Supplements: It is advisable to consult a nutritionist or doctor before purchasing any dietary supplements or health products.
- Reduce Intake of Fried or Grilled Foods: Build a balanced eating habit that includes a variety of nutrients.
- Maintain Regular Sleep and Manage Stress: Prevent hormone imbalances caused by stress and sleep deprivation.
Can Women with Uterine Fibroids Drink Coffee?
Women with uterine fibroids can drink coffee, but it should be done in moderation. The medical community generally agrees that excessive coffee consumption can lead to osteoporosis, so it is recommended that daily caffeine intake not exceed 300 milligrams.Dietary Guidelines for Patients with Uterine Fibroids
The dietary principles for individuals with uterine fibroids should focus on a high-fiber, low-fat, and low-sugar diet, with an emphasis on consuming antioxidant-rich foods:High-Calcium Foods: These are good for uterine development and ovarian health.
Increase Fruit and Vegetable Intake: Phytochemicals in plants can help reduce inflammation and inhibit tumor growth.
Consume Healthy Protein: This can regulate metabolic functions and promote normal hormone secretion, helping to prevent obesity.
Precautions and Frequently Asked Questions About Uterine Fibroids
Q: Who Needs Uterine Fibroid Surgery?
1. Individuals with significant fibroids symptoms caused by uterine fibroids that cannot be controlled with medication.2. Rapidly growing fibroids with suspicion of potential malignancy.
3. Fibroids that reach 7-8 cm in size, particularly in patients under 45 years of age who are not expected to undergo menopause within the next five years.
Q: What Should Women with Uterine Fibroids Consider When Trying to Conceive?
Schedule annual gynecological check-ups for monitoring.Begin pregnancy planning 3-6 months after undergoing hysteroscopic surgery.
Q: Is Recurrence of Uterine Fibroids Possible?
Yes, the recurrence rate for uterine fibroids is high. Approximately 10%-33% of patients may require additional surgery within five years after surgical removal. For patients with multiple fibroids, the recurrence rate may be as high as 70%.Q: Is It Possible for Uterine Fibroids to Expel Themselves?
It is highly unlikely for uterine fibroids to expel themselves. While fibroids may shrink due to reduced hormone levels after menopause, spontaneous expulsion does not occur.Successful Pregnancy Case of Uterine Fibroids at Lee Women’s Hospital
Ms. Yang, 36 years old, discovered an 8 cm uterine fibroid while undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment at Lee Women’s Hospital. The physician determined that the location of the fibroid would not affect embryo implantation, leading to the successful birth of her IVF baby. Subsequently, Ms. Yang underwent uterine fibroid removal surgery at Lee Women’s Hospital. 9 months after the surgery, she successfully conceived naturally and gave birth to her second daughter.Read more about the Great News (In Manderine):Woman conceived twins naturally after fibroid removal surgery.




