Knowledge Sharing
Can the causes of a blighted ovum be identified? How should you respond if symptoms of a blighted ovum occur?
When the inner cell mass of a blastocyst (the precursor of the fetus) experiences failed cell division or abnormal chromosome separation, the embryo may develop slowly or cease developing entirely. This results in what is commonly referred to as an "empty sac," clinically known as an "atrophic gestational sac" or "blighted ovum."
A blighted ovum typically occurs during the early stages of pregnancy, between 4 to 10 weeks, with an incidence rate of approximately 15% to 20%.
What You Need to Know about a Blighted Ovum:
What are the causes of a Blighted Ovum?
A Blighted Ovum is commonly caused by chromosomal abnormalities or genetic mutations in the embryo. Issues with the sperm or egg themselves, or problems during fertilization—even if both sperm and egg seem normal—can also contribute to this condition. Additionally, certain maternal health conditions or structural abnormalities of the uterus may increase the risk of a Blighted Ovum.
Possible causes of a blighted ovum include the following:
1. Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities are the most common cause of a blighted ovum. Errors occurring during the combination of sperm and egg may lead to improper chromosome distribution, making it impossible for the embryo to continue developing.
2. Advanced Maternal Age
As a woman's age increases, egg quality typically decreases, consequently elevating the risk of miscarriage.
3. Health Conditions
Maternal health conditions such as thyroid disorders, blood clotting disorders, or autoimmune diseases can indirectly affect embryo implantation and development.
4. Unhealthy Lifestyle Habits
Habits such as consuming alcohol, smoking, or drug use can negatively impact embryo development.
5. Poor Uterine Environment
Structural issues within the uterine cavity, uterine fibroids, or adenomyosis can create an unsuitable environment for embryo growth.
6. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal issues, such as insufficient progesterone (luteal phase deficiency), can prevent normal embryo development and implantation.
What are the symptoms of a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is typically detected during a prenatal check-up through an ultrasound scan. In most cases, a fetal heartbeat can be observed via transvaginal ultrasound between the 6th and 7th weeks of pregnancy.
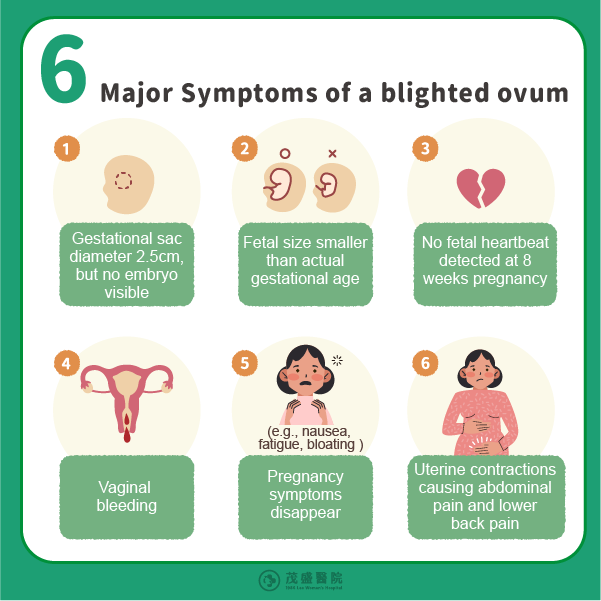
Common signs indicating a blighted ovum include:
- A gestational sac measuring 2.5 cm or more without a visible embryo on ultrasound.
- An embryo size that is noticeably smaller than expected for gestational age.
- No detectable fetal heartbeat after 8 weeks of pregnancy.
Additionally, pregnant women experiencing a blighted ovum may notice symptoms such as vaginal bleeding, sudden disappearance of early pregnancy symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness), and abdominal or lower back pain caused by uterine contractions.
Can a blighted ovum be detected through a pregnancy test?
Therefore, if you're concerned about a blighted ovum, the most accurate method is to visit a healthcare provider for an ultrasound examination rather than relying solely on a pregnancy test.
What are the options after discovering a blighted ovum?
1. Waiting for natural miscarriage
Once an embryo stops developing, hormone levels associated with pregnancy decrease naturally, leading to spontaneous miscarriage. The advantages and disadvantages of this method include:
【Advantages】:No need for surgery or medication such as RU486, causing less physical impact on the uterus and preserving future fertility.
【Disadvantages】:Intense uterine contractions and abdominal pain may occur as the embryo is expelled naturally.
The timing of natural miscarriage can be unpredictable, sometimes taking weeks to occur.
Risk of incomplete miscarriage leading to potential infection or complications, possibly necessitating medical intervention.
2. Medication-Induced Miscarriage
Medications such as uterine contractile agents (RU486 and/or Cytotec) can be used to enhance uterine contractions, promoting the expulsion of the embryo.
【Advantages】:No surgical risk and less damage to the uterus.
【Disadvantages】:More suitable for pregnancies within 7 weeks of development.
Not recommended for individuals with certain medical histories, drug allergies, or smoking habits.
Intense uterine contractions and discomfort may occur during the embryo expulsion process.
Medication-induced miscarriage carries a 5%-10% chance of failure; if unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be required for complete removal.
3. Surgical Removal
Embryo removal from the uterus can be performed through procedures such as dilation and curettage (D&C) or vacuum aspiration.
【Advantages】:Low failure rate and short procedure duration.
【Disadvantages】:Higher risk of uterine injury compared to non-surgical options.
Possible surgical or postoperative complications, including infection, bleeding, and damage to the endometrium.
Severe complications might increase the risk of future infertility.
How can the risk of a blighted ovum be reduced?
Performing PGT-A (Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy) can help identify healthy embryos, effectively reducing miscarriage rates.
The causes of fetal arrest and miscarriage are complex, but advanced maternal age and poor embryo quality are major contributing factors, often resulting in genetic and chromosomal abnormalities. Performing PGT-A (PGS) can help select healthy embryos. If you're aiming to improve IVF success rates, selecting high-quality embryos through PGT-A testing is essential.
Further Reading:What is Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS/PGT-A)? Is PGS testing necessary?
How to check if an embryo is developing normally?
Regular prenatal ultrasound examinations are essential for pregnant women, as they provide critical information such as embryo development, embryo size, fetal heartbeat, and gestational age. Early ultrasound can also detect abnormalities in embryo development, including a Blighted Ovum, ectopic pregnancy, and missed miscarriage. Thus, expectant mothers are strongly recommended to attend routine prenatal check-ups to monitor and ensure healthy fetal development.
More advanced fetal screening methods can also be conducted during pregnancy:
- Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): Detects fetal chromosomal abnormalities through maternal blood samples.
- Genetic screening: Identifies specific genetic disorders that might impact fetal health.
- Amniocentesis: Involves extracting amniotic fluid to assess fetal chromosomes and detect genetic anomalies.
- Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA): Provides detailed chromosome-level information, detecting more subtle abnormalities compared to traditional tests.
What Else Should You Know About A Blighted Ovum?
1. Does a blighted ovum cause bleeding?
A blighted ovum may indeed be accompanied by bleeding. When the embryo stops developing and gradually starts to naturally expel from the body, vaginal bleeding can occur. However, some women with a blighted ovum may not experience any bleeding at all. If no bleeding is observed after a certain period of monitoring, medical or surgical intervention may be needed to remove the non-viable pregnancy tissue from the uterus.
2. Will a blighted ovum pass naturally without medical intervention?
In some cases, women with a blighted ovum may naturally pass the pregnancy tissue as it detaches from the uterine lining, often accompanied by uterine contractions. This process typically takes about one to two weeks to complete.
3. Does a blighted ovum affect future chances of pregnancy?
A blighted ovum does not impact future pregnancy chances.
Therefore, women who have previously experienced a blighted ovum should not be overly concerned about its effect on their fertility. Factors primarily affecting pregnancy chances include age, lifestyle, egg and sperm quality, and overall reproductive health. To enhance the probability of a successful pregnancy, it is recommended to cultivate healthy habits and aim to conceive within the optimal fertility age window of 20 to 35 years old, thus maximizing the likelihood of a smooth and healthy pregnancy.
Concerned about a blighted ovum?
<< Contact us >>
For overseas patients, please leave a message below or Email to ivftaiwan@gmail.com
For patients in Hong Kong and Macau, please Email to ivftaiwan.hk@gmail.com
For patients in China, please add our official WeChat account: ivftaiwan01
★Any immediate or urgent inquiry, please dial +886-4-22347057 #1324




