Treatments
Reproductive Technique
-
Genetic Screening: PGT-A / PGT-M / PGT-SR
The laboratory is equipped with highly practical instruments, including next-generation sequencing (NGS), biochip microarray laser scanner, and polymerase chain reaction machines, to provide safe and accurate reproductive medical testing services with professional techniques and high-standard equipment. The main scope of testing includes preimplantation genetic testing for the monogenic disease (PGT-M, formerly known as PGD), preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (PGT-A, formerly known as PGS), and preimplantation genetic testing for structural chromosomal rearrangements (PGT-SR), aiming to improve embryo implantation rate and pregnancy rate.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidies (PGT-A/PGS)
Applicable for:- Maternal age of 35 and above
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Multiple failed embryo implantations
- Family history of chromosomal abnormalities
- Those seeking to avoid fetal chromosomal abnormalities
- Patients with hereditary diseases

▲PGT-A using next-generation sequencing technology
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic Disease (PGT-M/PGD)
Applicable for:- Alpha and beta thalassemia gene testing
- Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 gene testing
- Polycystic kidney disease gene testing
- Fabry disease Ankylosing spondylitis
- Customized familial genetic disorder testing services

▲Whole genome amplification, gene mutation detection, gene chip testing
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Structural Chromosomal Rearrangements (PGT-SR)
Applicable for:- Recurrent miscarriages
- Known carriers of chromosomal abnormalities
PGT-A PGT-SR PGT-M Testing Purposes Chromosomal Aneuploidy Chromosomal Structural Rearrangements Single Gene Disorders Applicable for Advanced maternal age (35 years and above)
Recurrent miscarriages
Family history of chromosomal abnormalities or translocations
Recurrent IVF failuresRecurrent miscarriages
Known carriers of chromosomal abnormalitiesKnown carriers of genetic diseases Diseases Tested Down syndrome
Turner syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome
Edwards syndrome
Patau syndromeRobertsonian translocation
Chromosomal translocationHemophilia
Thalassemia
Ankylosing spondylitis
Achondroplasia
Spinal muscular atrophy -
Embryo Culturing
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Commonly known as "test-tube baby," it refers to the cultivation of eggs and sperm in a laboratory dish to achieve fertilization.
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
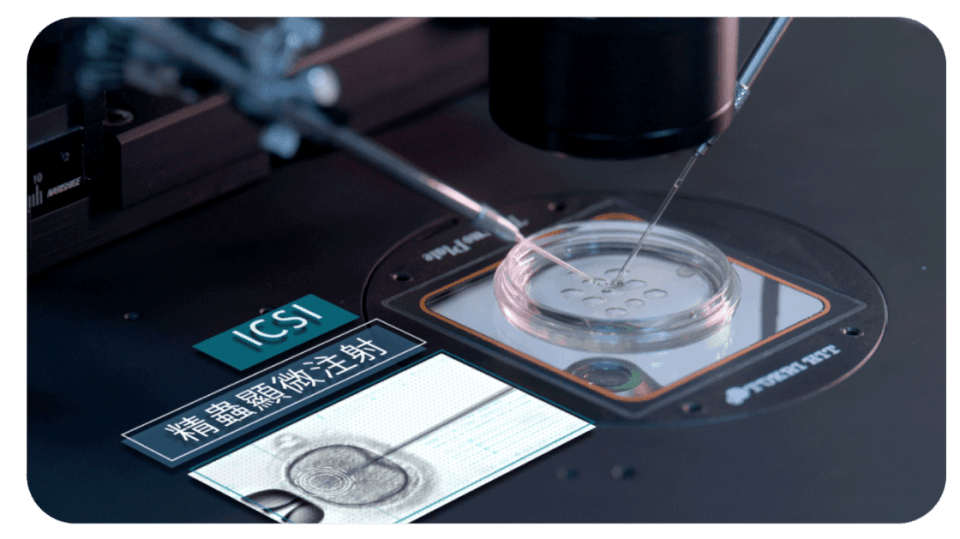

For patients with infertility, this technique uses microsurgical procedures to directly inject visually normal and motile sperm into mature eggs to achieve fertilization.
Embryo Morphokinetic Evaluation
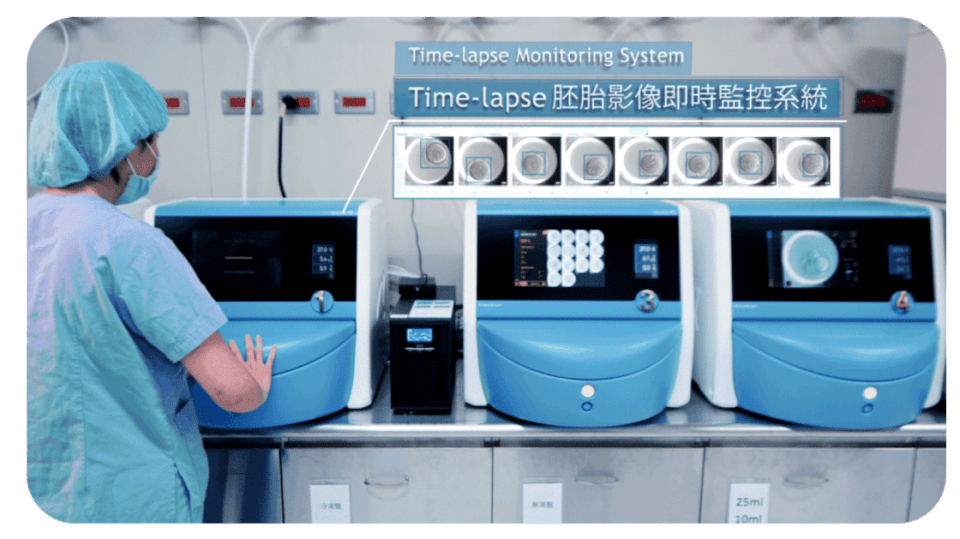

Using a time-lapse embryo imaging system, continuous monitoring of embryo development is performed, and embryo morphology is observed using embryo kinetic analysis software. This technology not only allows for comparison of embryo appearance but also provides valuable information on embryo division dynamics to select the most viable embryo for transfer, thereby increasing the chances of pregnancy.
Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH)
Laser assisted hatching is a technique where a small hole is made on the zona pellucida (transparent layer) of the embryo on the fourth day, facilitating implantation of the embryo in the uterine lining. This technique has been proven to increase the chances of conception for women of advanced age or those who have experienced multiple IVF failures. We use laser technology for precise, safe, and efficient drilling on the zona pellucida during embryo assistance hatching.
▲Appropriate cutting on the zona pellucida using laser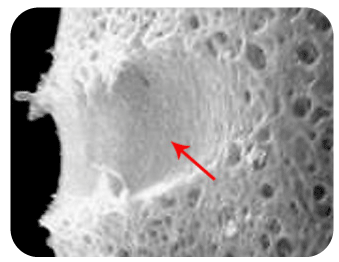
▲Magnification of Laser assisted embryo hatchingSpindle View Technique
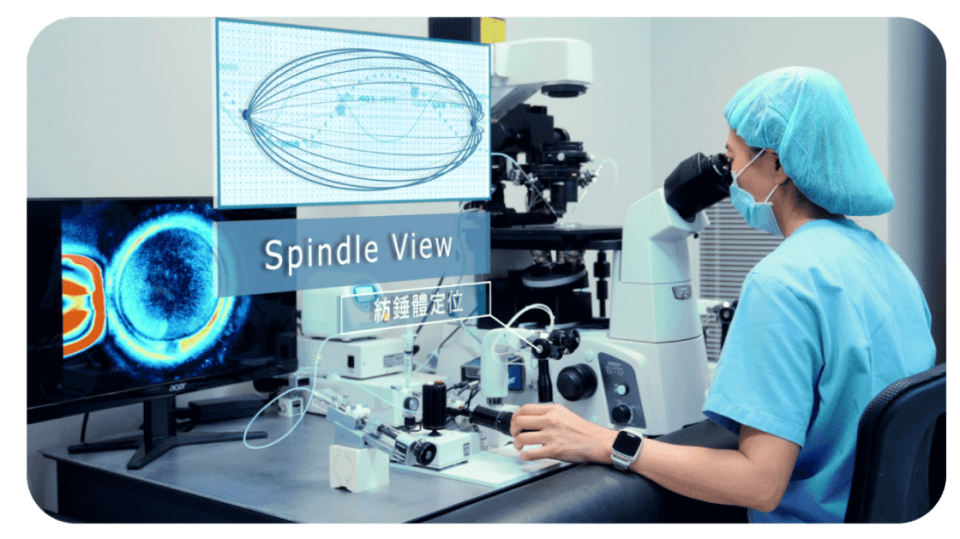
The spindle plays a crucial role in the process of cell division as it guides the movement of chromosomes. Therefore, when the spindle is damaged, it can potentially affect embryo development or result in chromosomal abnormalities. To address the phenomenon of spindle displacement that may occur in older patients, we use polarized light microscopy to accurately locate the spindle. This ensures that during intracytoplasmic sperm injection, the chromosomes on the spindle are not damaged, thus facilitating successful fertilization.
Cryopreservation by Vitrification

Vitrification is a specialized freezing technique that involves using high concentrations of cryoprotectants to rapidly dehydrate embryo cells within a short period. The embryos are then cooled at an ultra-rapid rate of approximately -23,000°C per minute to prevent ice crystal formation, resulting in the embryos reaching a glass-like state. This process requires skilled embryologists with extensive experience to minimize demage through proficient techniques. -
Male Fertility Testing
Sperm Analysis
Sperm analysis is performed to assess the quality of sperm, including measuring the volume of semen (normal range: 1.5 milliliters), sperm concentration (normal range: 15 million per milliliter), sperm motility (normal range: 42%), progressive motility (normal range: 30%), sperm viability (normal range: 54%), and normal sperm morphology (normal range: 4%). It also examines the presence of white blood cells in the semen (normal value: < 1 million per milliliter) and checks for sperm agglutination.
Lee Women's Hospital utilizes Computer-Assisted Sperm Analysis (CASA) for sperm analysis. CASA is a computer-based system that combines computer and video imaging for automated sperm detection. It provides detailed, accurate, fast, and comprehensive reports on sperm analysis, including sperm count, motility, velocity, linearity, and amplitude. Advanced sperm motion analysis software has been developed, which not only quantifies sperm motility but also automatically identifies sperm morphology.
Hyaluronan Binding Assay (HBA)
Hyaluronan binding assay is a functional test used to predict the fertilization capacity of sperm. In the natural fertilization process, freshly released human eggs are surrounded by cumulus cells, and hyaluronan is a major component of the extracellular matrix of cumulus cells. Hyaluronan can chemically attract and trigger the activation reaction (hyperactivation) of sperm. Only mature sperm can bind to hyaluronan. Therefore, by assessing the efficiency of sperm binding to hyaluronan through HBA (normal value: > 80%), it can be determined whether the sperm is mature and has normal physiological function. Clinically, this test can further predict the fertilization capacity of sperm with eggs.

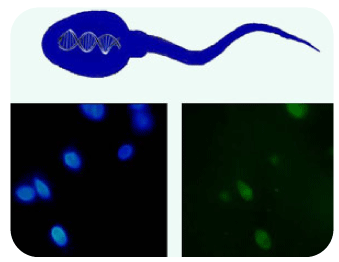
▲Hyaluronan Binding Analysis Kit for Sperm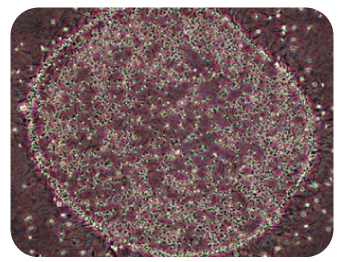
▲Analysis of Sperm-Hyaluronan Binding EfficiencySperm Cryopreservation
Sperm cryopreservation involves the freezing and storage of sperm samples for various purposes, including husbands participating in assisted reproductive treatments, preventive sperm storage (e.g., in case of accidents), sperm storage before cancer patients undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy, or sperm storage before male sterilization. Through a process of pure sperm washing, viable sperm is separated and purified from the semen sample. For those who require long-term storage, these viable sperm are frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen using appropriate cooling methods and cryoprotectants. When needed, they can be thawed and used following appropriate procedures.
Sperm DNA
Using molecular biology techniques, this panel is used to diagnose the causes of male infertility. The examination includes testing for Y chromosome gene microdeletions in cases of oligozoospermia or azoospermia, and detection of sperm DNA fragmentation.