Knowledge Sharing
Menstrual Cycle: How to calculate the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle, defined as the regular pattern of reproductive events, refers to the series of physiological changes that occur in a woman's body from the first day of menstruation to the day before the next menstrual period.
The average menstrual cycle length for most women is between 21 and 35 days, with a normal menstrual cycle length of 28 days and a menstrual period lasting 4 to 7 days.
During the phase of the menstrual cycle, women experience different stages known as the follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation.Some may also refer to these stages as the fertile period or safe period when calculating conception for contraception or pregnancy planning.
This article will provide you with a deeper understanding of the process and changes that occur during each stage of the menstrual cycle, methods for calculating the menstrual cycle, and what constitutes an irregular or abnormal menstrual cycle.
About Menstrual Cycle
- What are the stages of a complete menstrual cycle?
- How to calculate the menstrual cycle?
- What is an irregular period? What causes menstrual irregularities?
- What Causes Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
- How can irregular periods affect your daily life?
- What Tests Should Be Done for an Irregular Menstrual Cycle?
- Does menstrual irregularity affect the ability to get pregnant?
What are the stages of a complete menstrual cycle?
How do we define a complete menstrual cycle? It starts on the first day of menstrual bleeding and continues until the day before the next menstrual period, typically falling within a range of 21 to 35 days.The menstrual cycle goes through four stages: follicular phase ➜ ovulation ➜ luteal phase ➜ menstruation.
We will use an average 28-day menstrual cycle as an example for the following explanation.
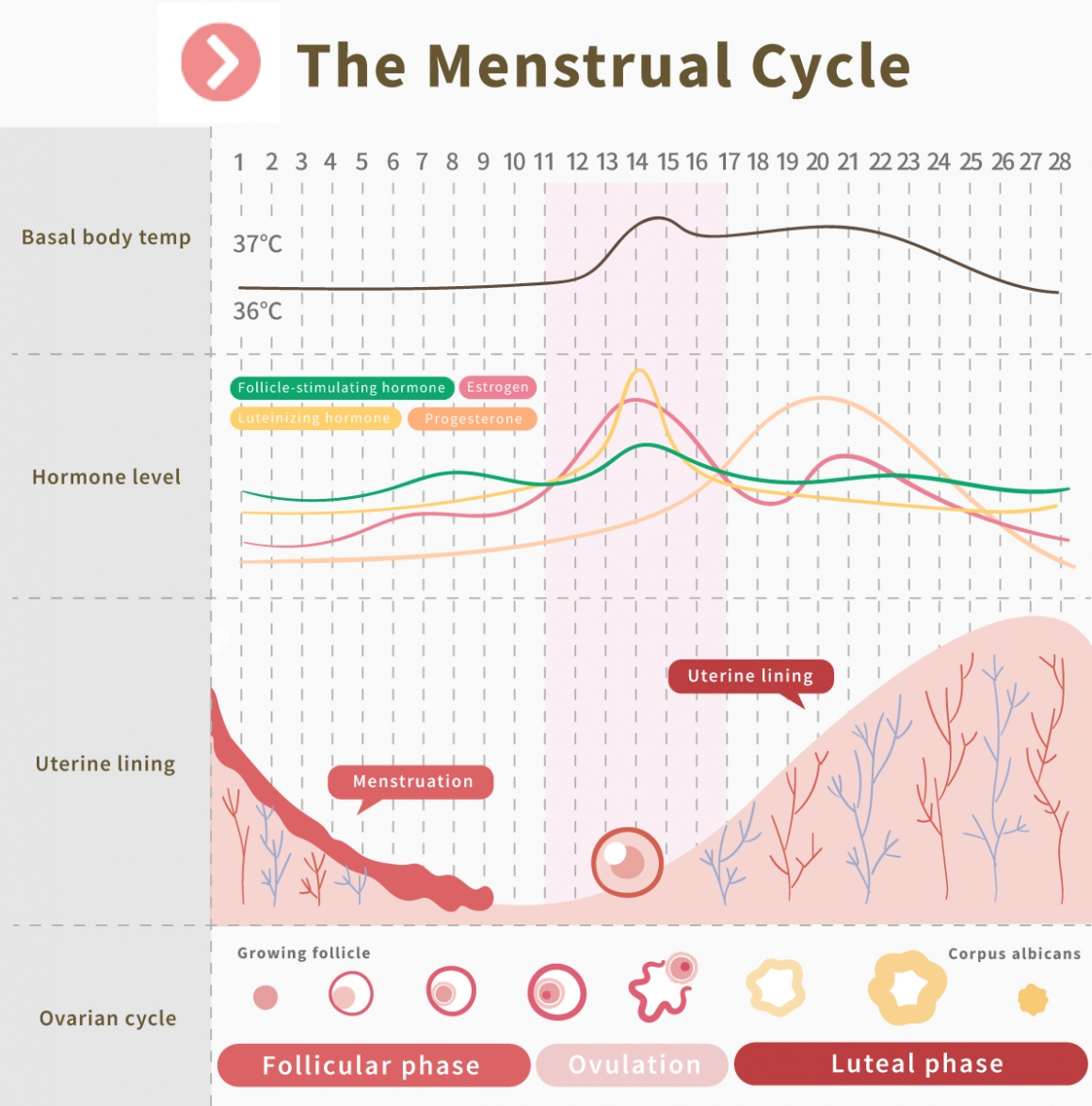
Follicular phase:
Under the influence of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), several small follicles begin to develop within the ovaries. Only one dominant follicle will mature, while the remaining follicles will stop growing.The dominant follicle continues to grow and develop into an egg. The estrogen secreted by the follicle, along with other estrogen hormones, thickens the uterine lining.
Ovulation:
Once the egg is released from the ovary caused by the peak of luteinizing hormones, it stays in the fallopian tube for 24-48 hours. The remaining follicles in the ovary form the corpus luteum, which secretes estrogen and progesterone (P4). These hormones maintain the thickened uterine lining.Luteal phase:
After the egg is released from the ovary, it stays in the fallopian tube for 24-48 hours. The remaining follicles in the ovary form the corpus luteum, which secretes estrogen and progesterone (P4). These hormones maintain the thickened uterine lining.Menstruation:
Due to high levels of estrogen and progesterone, a feedback mechanism suppresses the secretion of FSH and LH by the pituitary gland. The corpus luteum subsequently shrinks, leading to a rapid decrease in progesterone and estrogen. As a result, the uterine lining, which no longer receives these hormones, begins to shed, resulting in menstrual bleeding.Learn more about ovulation:
Is bleeding or discharge a sign of ovulation? Calculating ovulation and predicting ovulation to accurately determine the timing.
What are the symptoms of ovulation bleeding?
How to calculate the menstrual cycle?
How can we calculate the regular menstrual cycle?
There are various online menstrual cycle calculators and tools available. But why do we need to calculate the menstrual cycle? Couples planning for pregnancy can use menstrual cycle calculations to predict ovulation. Women without pregnancy plans can use it to understand their own body's status.
For most women, the menstrual cycle is regular and cyclic, making the calculation relatively straightforward. By accurately recording the first day of menstrual bleeding, we can easily determine the menstrual cycle. Let's follow these steps to track your menstrual cycle:
1. Record the day of menstruation
Recording the date of menstruation for each month is the first step in calculating the menstrual cycle. The number of days from the first day of menstruation to the day before the next menstrual period represents the complete menstrual cycle. For example, if the period starts on September 1st and the next period arrives on September 30th, the menstrual cycle length is 29 days.2. Calculate the average menstrual cycle length
By recording your menstrual cycle for at least three consecutive months, you can calculate the average length of your menstrual cycle.3. Calculate the next expected period
Once you have calculated the average menstrual cycle length, you can use it to estimate the possible date of your next menstrual period based on your cycle's pattern.Every individual's menstrual cycle length and duration may vary slightly. However, as long as it falls within the mentioned range of days and follows a regular pattern, it is considered a normal menstrual cycle. During menstruation, it is normal to experience symptoms such as dizziness, headache, lower back pain, breast swelling, abdominal discomfort, edema, and gastrointestinal issues.
What is an irregular period? What causes menstrual irregularities?
Once you understand how to calculate your menstrual cycle, you can observe whether your monthly cycles are regular. Sometimes, due to changes in lifestyle, personal emotions, or stress, menstrual bleeding timing may deviate from the calculated average menstrual cycle.However, is a one-day delay considered irregular? In fact, as long as the timing falls within a range of ±7 days, it is considered normal, and there is no need to be overly concerned.
What conditions indicate an abnormal or irregular menstrual cycle?
On average, a woman's menstrual cycle ranges from 21 to 35 days, with menstrual bleeding lasting 4 to 7 days. If the following conditions occur, it indicates symptoms of irregular menstrual cycles:Prolonged menstrual cycles (>45 days)
When the menstrual cycle exceeds 45 days, it may be due to hormonal imbalances or ovarian dysfunction. Most patients experience anovulatory menstrual cycle, which can affect fertility, with only a few still experiencing normal ovulation. If a woman has experienced prolonged menstrual cycles for 1 to 2 months, it is recommended to visit a hospital for hormone testing.Shortened menstrual cycles(<21 days)
When the menstrual cycle is shorter than 21 days, it may be caused by excessive stress, ovarian dysfunction, or inadequate progesterone secretion. Insufficient progesterone secretion leads to a short duration between menstruation and ovulation. Additionally, a shortened menstrual cycle indicates ineffective thickening of the uterine lining, which can lead to difficulties getting pregnant or miscarriages.For women planning for pregnancy who observe a short or suddenly shortened menstrual cycle, medical examinations are recommended.
Causes of menstrual cycle irregularities:
The menstrual cycle in women is controlled by the interaction of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries, which secrete hormones. Therefore, any abnormalities in these organs can affect the menstrual cycle. Additionally, mental stress or excessive dieting can also cause menstrual irregularities.- Hormonal imbalances
- Uterine tumors
- Thyroid abnormalities
- Liver dysfunction
- Coagulation disorders
- Unhealthy lifestyle habits
What Causes Irregular Menstrual Cycles?
Irregularities in the menstrual cycle can occur due to hormonal factors, lifestyle changes, and physical health conditions that affect the physiological rhythm of menstruation. Additionally, during the first two years after menarche (the onset of menstruation), irregular menstrual cycles are more common due to unstable hormone secretion.| Possible causes of irregular menstrual cycles |
|
|---|---|
| Stages where irregular menstrual cycles may occur |
|
How can irregular periods affect your daily life?
Having an irregular menstrual cycle can cause various difficulties in daily life. During menstruation, apart from the need to regularly change sanitary products, it is often accompanied by physical discomfort. If the menstrual cycle is irregular and it is difficult to predict the onset of menstruation in advance, it may disrupt plans for important events such as exams, business trips, travel, or weddings.Furthermore, the inability to calculate the safe and fertile periods of the menstrual cycle can affect contraception or family planning. This makes it challenging to plan accordingly based on the physiological cycle.
What Tests Should Be Done for an Irregular Menstrual Cycle?
If a woman experiences menstrual irregularities or abnormalities, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist at a hospital. The physician will inquire about the complete medical history and family history to rule out pregnancy and malignant tumors.Relevant tests for an irregular menstrual cycle may include:
- Blood tests: To examine clotting function and detect anemia.
- Gynecological ultrasound: To assess structural issues in the uterus, endometrium, and ovaries.
Does menstrual irregularity affect the ability to get pregnant?
The menstrual cycle reflects a woman's overall health status, and while menstrual irregularity does not equate to infertility, it can indicate weakened uterine function. Menstrual irregularities may be a precursor to ovarian disorders, such as:- Premature ovarian failure
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Endometriosis
- Chocolate cysts
Additionally, menstrual irregularities in women often accompany symptoms of hormonal imbalances, which can impact fertility and indicate abnormalities in the endocrine system.
Irregular menstrual cycles are a common complaint among patients with infertility. Irregular periods may be related to ovulation issues, leading to decreased natural conception rates and even female infertility. If there are concerns about menstrual irregularities, it is advisable to undergo early evaluation and treatment to prevent any negative effects on fertility.




